- Главная
-
Учебник
- DIALux 4
- DIALux evo
- IES
- Форум
- Галерея
- Блоги
-
Скачать
- DIALux
- Базы
- Плагины
- 3D модели
- Текстуры
- Книги
-
Новости
Street Valuation Fields in Exterior Scenes
5 сентября 2012 - АдминDIALux users often expressed their wish to use “real” situations for street lighting planning. That is not possible in a design according to EN 13201 or the obsolete DIN 5044. The “standard street” does not encompass curves or the possibility of changing single luminaire technical values or positions. So we added a new calculation surface for exterior scenes to DIALux, which calculates the luminance distribution on a roadway for an observer: the Street Valuation Field. This calculation considers exactly all luminaires and other objects placed in the exterior scene. Indirect light, e.g. reflections from facades, is not considered, shadowing through trees or buildings is. Because of the strict definitions of street lighting standards, the results of a Street Valuation Field should be used with extreme caution regarding the limitations of EN 13201. Whereas the “standard street” considers a certain amount of luminaires in a line in front and behind a single calculation point, the new calculation surface considers all luminaires in the exterior scene, even luminaires with other tasks.

Fig. 311 Calculation surface Street-valuation field
A Street Valuation Field consists of two parts: the calculation surface itself and a corresponding observer. The surface is visible in CAD windows and can be changed as needed. It can even be polygonal. The observer position and his viewing direction define the calculation grid of the surface. This grid is displayed by little crosses in the CAD. Grid point counts are able to be changed; initially there are 10 x 3 grid points. Initially the observer is placed 60 m to the left from the start of the surface. This is the observer position in a “standard street”. The position can be changed as needed. His viewing direction is 0° that is in direction of the positive X-axis. Therefore the grid points are initially parallel to the X-axis as well.
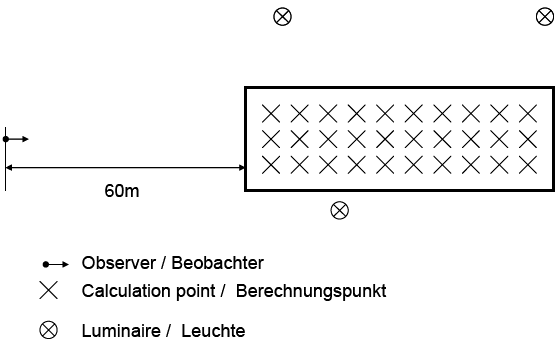
Fig. 312 Simple Street-valuation field in an exterior scene
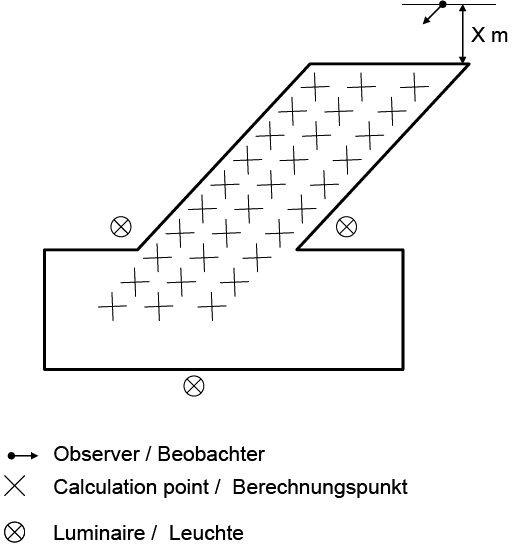
Fig. 313 Complex Street-valuation field in an exterior scene
The first graphic shows a simple example for Street Valuation Fields. It is very close to a “standard street” from EN 13201, only luminaire positions are different. The second graphic shows a more complex example. The observer is placed in the side street and views towards the crossing. His viewing direction (ca. 225°) defines the calculation grid’s orientation.
Note: Reflection properties of tarmacs are only defined for close sectors. If the observer is placed too close to or too far away from the surface, no luminances can be calculated.Рейтинг: 0 Голосов: 0 6603 просмотраКомментарии (0)Manual
